Partial Discharge: Detection, Location & Continuous Monitoring of Transformers
Partial Discharge (PD) measurements allow you to assess the health of an insulation system using non-invasive measurement and analysis methods. While partial discharge is a widely used, accepted and standardized tool in factory acceptance testing, field testing and in-service applications have become increasingly important, as they allow continued assessment of the health of a transformer’s insulation system throughout its life.
Various measurement approaches are used, either standalone or in combination, to identify potential problems within a transformer’s insulation system.
These methods include:
- High frequency current transformers connected to ground connections of the transformer
- Bushing tap and bushing monitor PD sensors measuring PD via the bushing tap capacitances
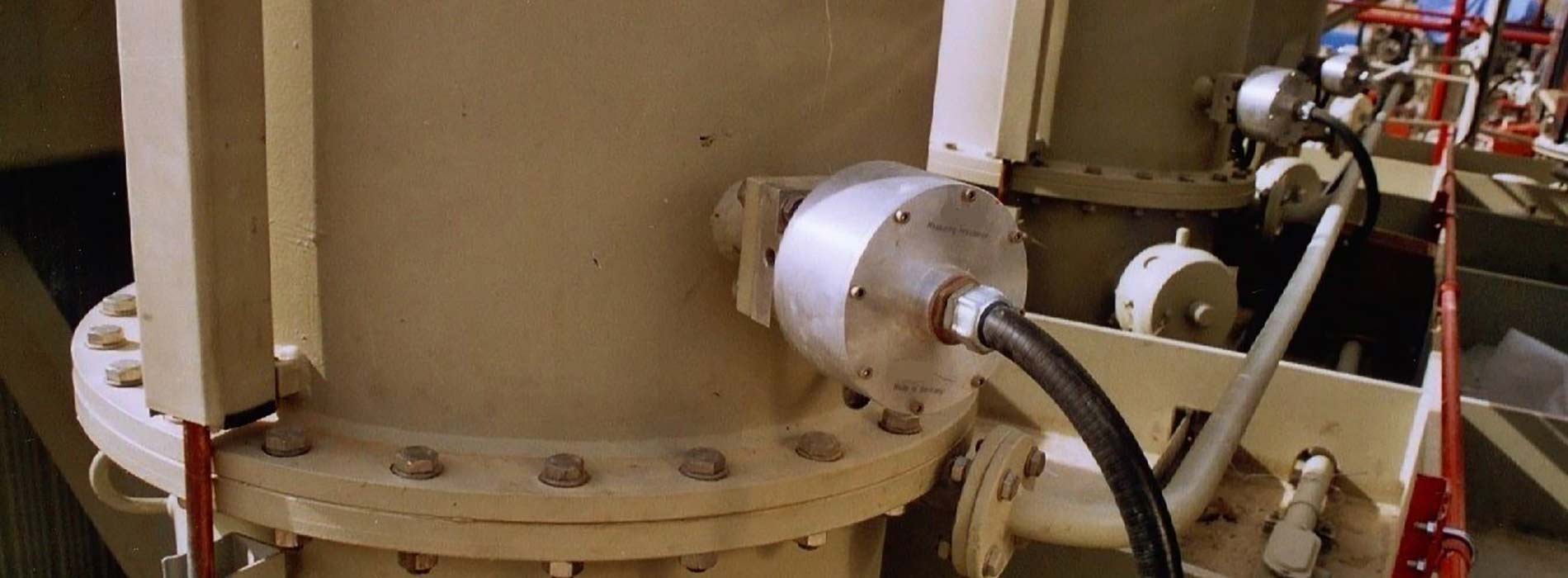
- UHF drain valve antennas inserted into the transformer tank in service via the drain valve
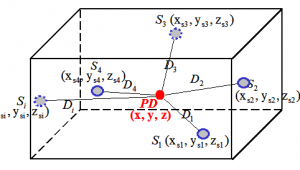
- Acoustic PD detection to determine the geometric location of PD sources within a transformer
Measurement systems acquiring measurement data using the sensing methods mentioned above vary depending on application, requirements and the transformer under test. They range from simple survey tools to sophisticated partial discharge analyzers and permanent monitoring systems.
Any assessment of PD in transformer insulation systems depends on a range of applied measurement methods contributing to the analysis. PD measurement methods allow identification of different types of defects, phase association, trending and history as well as geometric location.